Challenges
At present, adhesive residues are the main obstacle to recycling wood fibers. Up to 60 percent of collected wood waste is contaminated. The urea-formaldehyde adhesives currently in use make recycling difficult, primarily due to their cross-linked polymer structure, and also reduce the quality of the wood fibers through chemical contamination.
Objectives and project plan
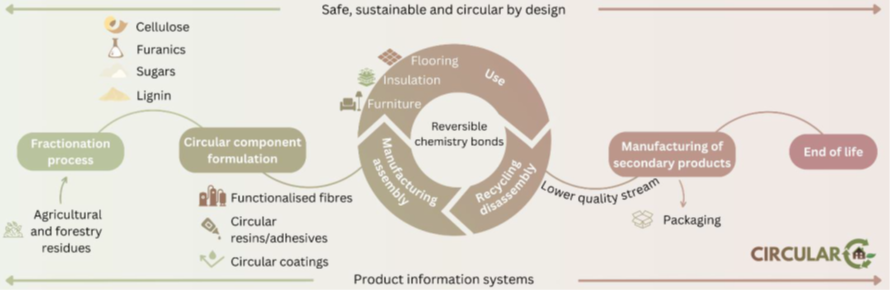
The CIRCULAR-C project aims to develop recyclable, sustainable bio-based adhesives, coatings, and functionalized fibers that are suitable for wood panels in flooring and furniture as well as for insulation materials. The formulations will be developed according to the principles of Safe and Sustainable by Design (SSbD). Another component is the inclusion of digital product passports and investigations into recycling and secondary recycling as well as secondary market applications in order to consider circularity throughout the entire product life cycle.
Fraunhofer CBP will produce basic chemicals from renewable raw materials in the project. In the biomass fractionation group, wood and straw will be fractionated to obtain cellulose fibers and lignin as sustainable material components. The hemicellulose sugars are converted into furfural in the chemical processes group by reactive distillation. The refined cellulose will be applied in fibreboards, lignin will be used in insulation foams or, such as furfural, for the production of adhesives and coatings.
Impact
CIRCULAR-C aims to improve the recyclability of wood-based materials, make better use of residual materials through new recycling options, and reduce environmental impact and greenhouse gas emissions. The project is thus paving the way for a more sustainable and circular construction industry.

 Fraunhofer Center for Chemical-Biotechnological Processes CBP
Fraunhofer Center for Chemical-Biotechnological Processes CBP