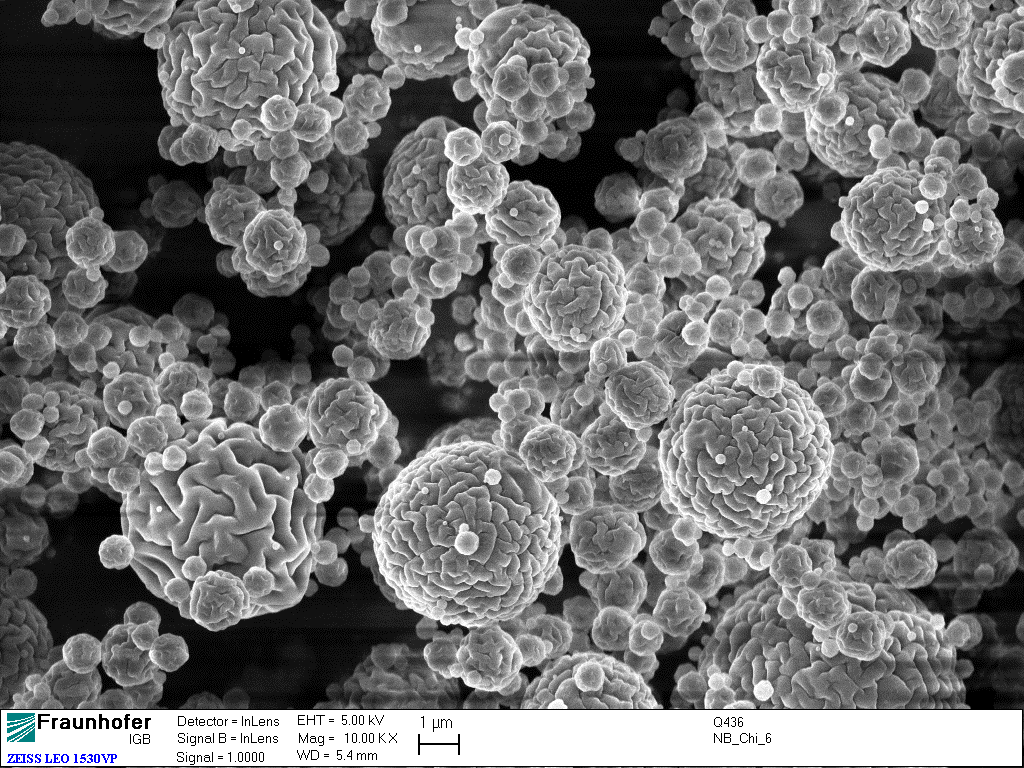
Encapsulation of active ingredients and effect substances
This means that we encapsulate the active ingredient in polymer-based functional nano- or microparticles. Encapsulation allows us to "package" low-molecular substances such as fragrances or vitamins, but also proteins, antibodies and enzymes - while fully preserving their (bio)activity. Encapsulation enables the formation of a three-dimensional protective space for the active ingredient, as it is separated from its micro-environment by the surrounding shell. In this way, sensitive substances can be protected from oxidation, for example, and reactive agents from chemical reactions.
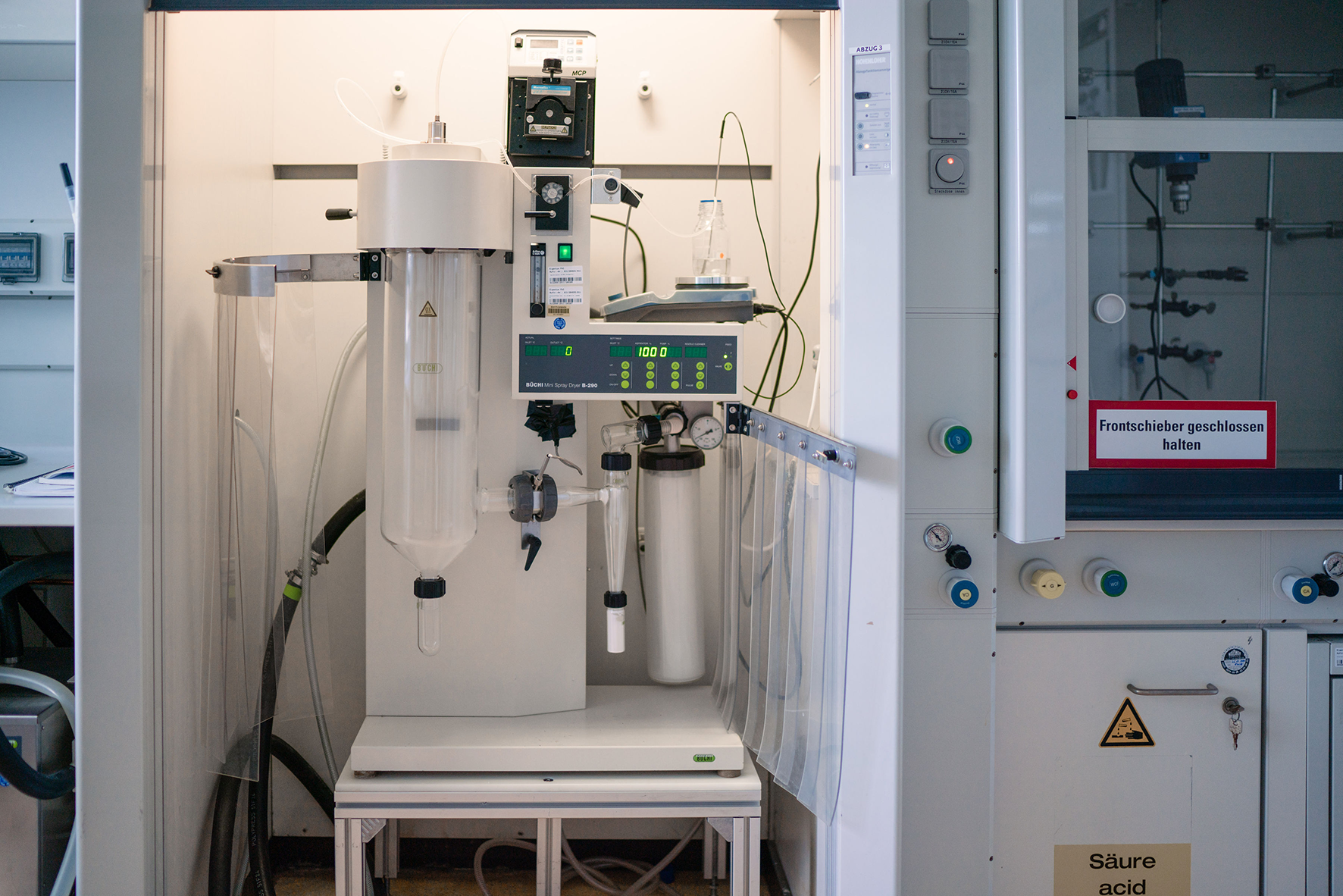
Spray drying
Spray drying is an established process in many industrial sectors such as pharmaceuticals, food science, chemistry and materials science. A solution, suspension or emulsion is converted into a solid powder form in a single process step. Especially for sensitive substances such as hormones, proteins or vitamins, spray drying is a very gentle method of drying and is also suitable for microencapsulation
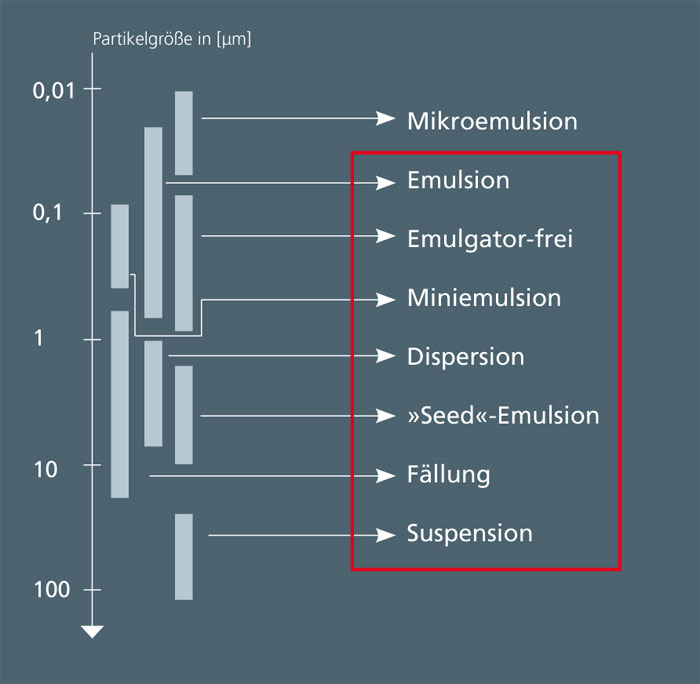
Polymerization techniques
At the Fraunhofer IGB, customer-specific nano- and microparticles in the range of 200 nm – 10 μm are produced from commercially available polymers, depending on the problem at hand. Various polymerization techniques are used, such as miniemulsion polymerization or emulsifier-free emulsion polymerization.
Adjusting the release kinetics
By varying the particle size, the degree of loading, the molecular weight and the ratio of hydrophilic and hydrophobic monomer units, we can influence the release kinetics of the encapsulated substances in a customized manner. In this way, releases over very long periods (Ultralong Drug Release, ULDr) of three to four months can also be realized. Biodegradable compounds are of particular interest here, as these are completely metabolized or decomposed after their application in the body or in the environment.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB
Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB