A key task in many processes in chemistry, pharmacy and biotechnology is the specific separation of molecules from mixtures, either to obtain or purify substances or to remove interfering accompanying substances. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles (Nanoscopic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers, NanoMIPs) act as artificial receptors and are excellently suited as adsorbers for solving these problems. Based on the lock-and-key principle, the nanoparticles specifically recognize biomolecules and active ingredients such as amino acids, peptides and proteins, but also low-molecular compounds or interfering substances such as toxins and substances with endocrine effects.
Advantages of the NANOCYTES® technology
Molecular recognition function modeled on nature
In nature, information is transmitted through material contact: hormones dock onto specific receptors and trigger precise signals. Or harmful substances are recognized in an organism by antibodies, masked and then eliminated.
These molecules behave like keys and locks, but are made of elastic building blocks (induced fit): Spatially defined chemical structures fit together like positive and negative imprints of the same chemical pattern. Nature has developed this principle into a fascinating range of applications. Due to the limited durability of natural receptors, they have to be continuously re-produced - a massive obstacle for technical applications.
Separation technology
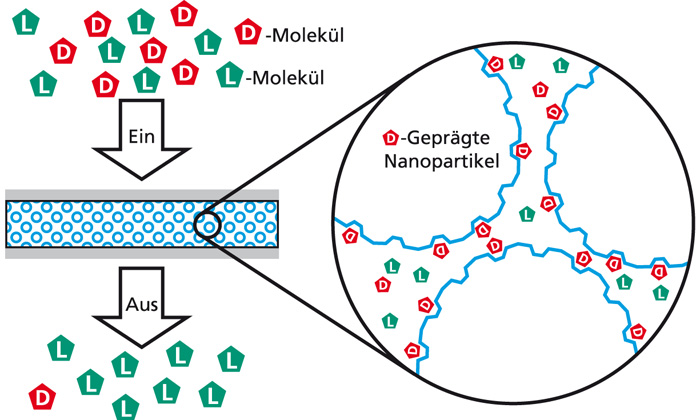
If the NanoMIPs are used as polymer particle suspensions, they can be equipped with a magnetizable core of magnetite for easier separation. This enables quick and easy separation by means of a magnetic separator.
Another possibility to use NanoMIPs as separation tools is to integrate the NanoMIPs as a selective element between two membranes. This creates a so-called sandwich composite membrane, which consists of a support and a cover membrane and the selective core, the layer of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles. NanoMIPs can also be directly integrated into polymer membranes as a selective element. In this case, they are added to the polymer solution directly during membrane production using phase inversion technology. The polymer solution, which forms the subsequent membrane structure and contains the molecularly imprinted particles, is then poured into the desired form.
Conclusion
The patented proprietary Fraunhofer technology makes it possible to eliminate previous weaknesses of molecular imprinting, such as lack of control over the morphology and chemical composition of the material produced. The applied method allows a much better control of the embossing process on the polymer surface. In addition, molecular imprinting in aqueous systems is made possible, which is the prerequisite for imprinting biological macromolecules.
NANOCYTES® technology is used to create artificial, nanostructured receptors that are predestined for applications in diagnostics, sensor technology and downstream processing. The molecularly imprinted polymer anomonolites can be modified, for example with magnetizable nuclei or dyes, depending on customer-specific requirements.
Advantages of the NanoMIPs
- High binding capacity
- High selectivity
- High chemical and thermal stability
- Regenerability and recyclability
- Cost-efficient manufacturing process
 Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB
Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB