The fermentation of organic residues is an alternative to waste recycling, in which biogas is a valuable energy source. While biowaste fermentation plants are widely used in Germany, this technology is not yet applied in Brazil. After collection, household waste in Brazil usually ends up in landfills together with other waste. Up to two thirds of Brazilian household waste consists of organic components. Energy recovery by converting the recoverable portion of organic waste into biogas is currently not practiced.
Anaerobic treatment of organic waste using the example of Brazil
Biogas and fertilizer from kitchen waste
As part of the BMBF-funded research project "Decentralized water supply and disposal combined with material and energy production under consideration of hygienic aspects for the Piracicaba region", Fraunhofer IGB has built a bioreactor plant for the fermentation of organic waste at the Departemento de Água e Esgoto (DAE) in Americana, a city in the state of São Paulo. It is used there for teaching and training purposes and for the determination of basic data. The plant is used for the anaerobic digestion of kitchen waste produced in the canteen of the waterworks at DAE. The anaerobic digestion process also significantly reduces the amount of remaining organic matter. The effluent from the plant is a valuable fertiliser, as both phosphorus and nitrogen as well as the mineral salts are retained during the anaerobic conversion. The resulting biogas is a regenerative energy source that can be used in practically the same way as natural gas.
Functional principle of the biowaste fermentation plant
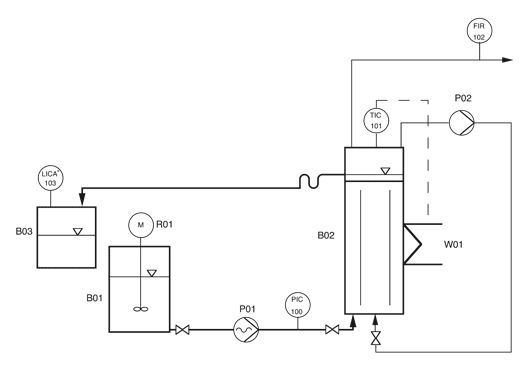

Picture (left) shows the scheme of the biowaste fermentation plant. To operate the plant, the material to be fermented is mashed to a maximum of 10 per cent solids content with the addition of water using a mixer and stored in storage vessel B01. The mixer mixes the contents of the vessel before and during each feed to the reactor. With the aid of the feed pump P01 (eccentric screw pump), the bioreactor B02 is periodically fed with the mashed organic waste several times a day. The bioreactor B02 is mixed by gas injection. The hydraulic residence time in the bioreactor is about 10 days. The bioreactor is tempered to about 30-37 °C by means of a heating/cooling thermostat (mesophilic operation), because in this temperature range an adapted anaerobic mixed population of microorganisms works optimally. The amount of biogas formed is registered by a gas meter. The entire control of the bioreactor plant is done by a programmable logic controller.
The plant is installed directly next to DAE's Environmental Education Centre. On the occasion of the "1º Seminário Internacional de Biotecnologia", organized by the Universidade Metodista de Piracicaba and the Fraunhofer IGB, an excursion to the "Biodigestor" took place on October 18, 2007.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB
Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB