The lignocellulose pulping process produces the (solid) cellulose fiber and the supernatant of the pulping solution, which among other things contains hemicellulose.
In the next step, the monomeric sugars are obtained from cellulose or hemicellulose. For this purpose, enzyme mixtures of cellulases or hemicellulases are used, which synergistically break down cellulose and hemicellulose into the sugars they contain (glucose or xylose).
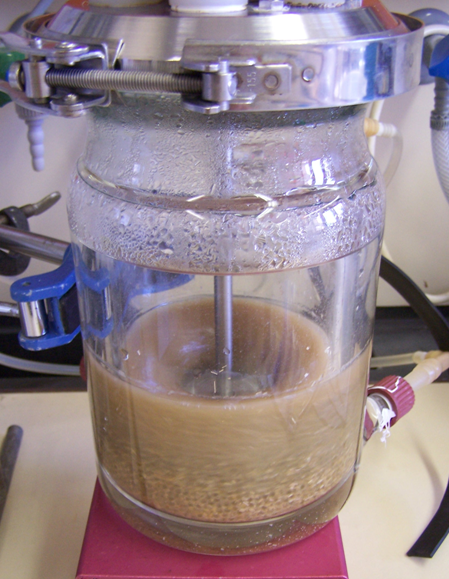
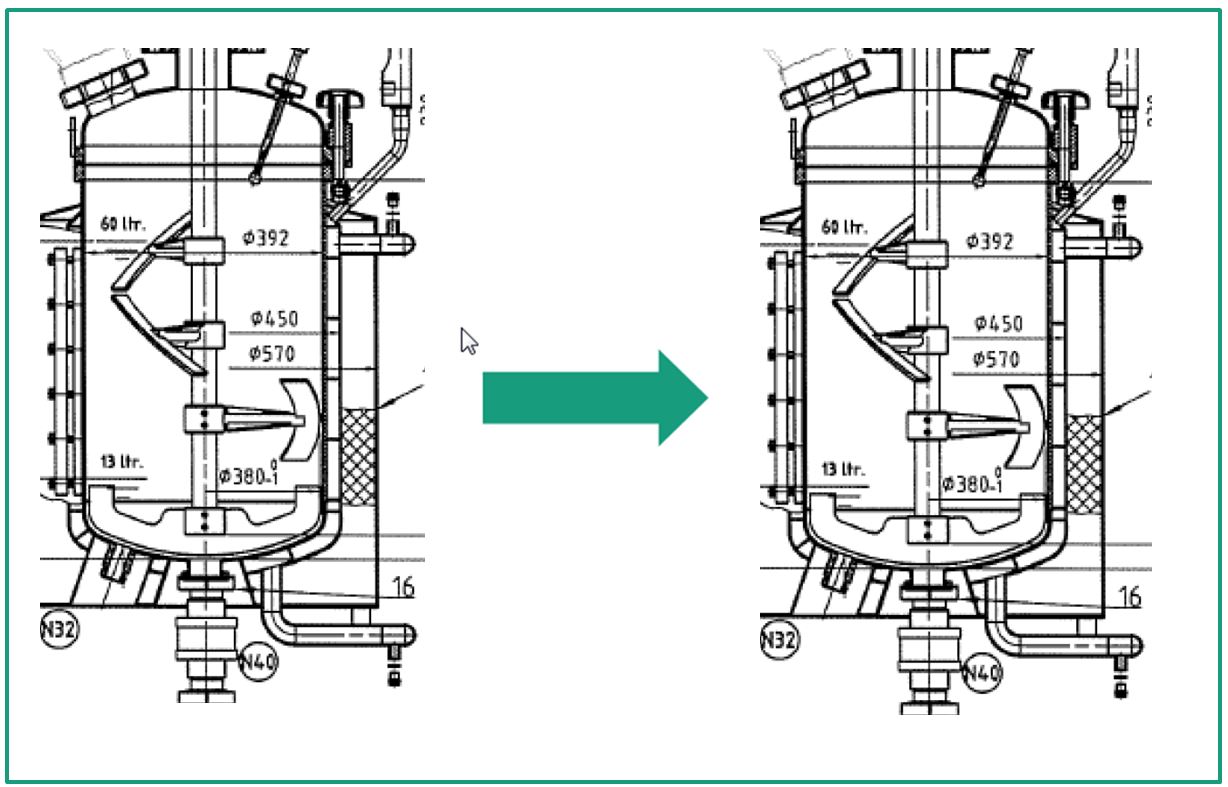
Powerful stirred reactor for hydrolysis of cellulose and hemicellulose to monomeric sugars
The uniform mixing of the enzymes in the pulp mass is of great importance for an optimal space-time yield of the hydrolysis process. To ensure this, we at the Fraunhofer IGB have developed a high-performance stirred reactor system that is characterized by its special stirrer geometry and is therefore suitable for mixing cellulose fiber pulp with up to 20 percent solids content. In this way we were able to achieve yields of > 100 g/kg glucose. A maximum yield of 70 percent over 48 hours was achieved with a minimum enzyme dosage.
This was followed by the design and construction of the reactor for the pilot plant in Leuna at Fraunhofer CBP.
Applications of lignocellulose-based sugars
The sugar solutions obtained are suitable for various applications. Glucose, for example, can be used as a substrate by a large number of microorganisms in fermentations.
The digestion solution rich in hemicelluloses can also be used for the fermentation of certain microorganisms, which was also part of the work at the Fraunhofer IGB. The digestion process may cause the digestion solution to contain toxic degradation products, which must be removed before use.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB
Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB